RESULTS
2-4 days
LONG-TERM EXPOSURE


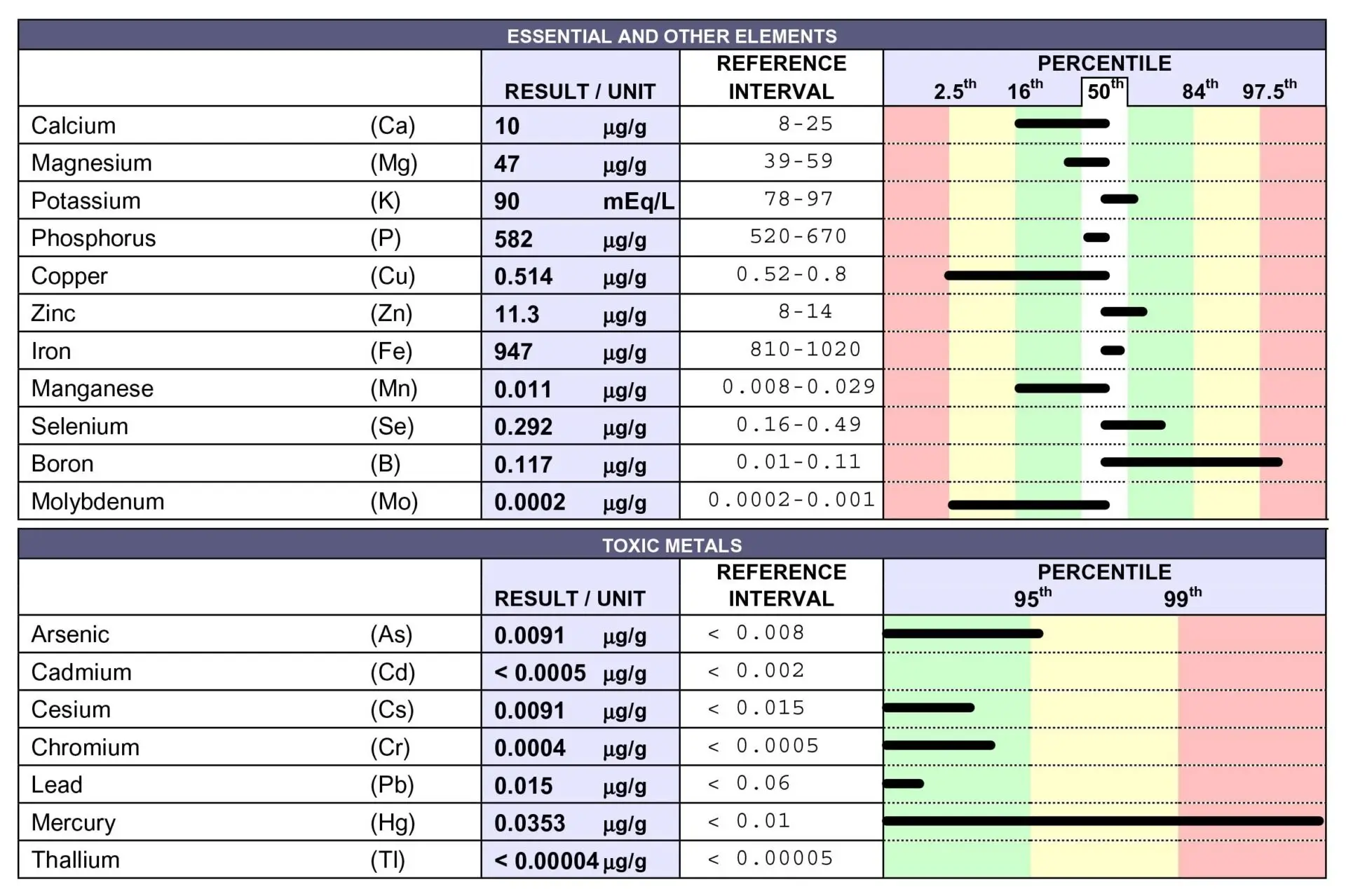
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Elements
This test determines the content of the following
minerals in the red blood cells (RBCs) of the test
subject. It is used for the assessment of ongoing, and
to some degree, recent exposure to the metals.
Metals Tested
Toxic
- Arsenic (As)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Cesium (Cs)
- Lead (Pb)
- Mercury (Hg)
- Thallium (Tl)
Essential/Beneficial
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Potassium (K)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)